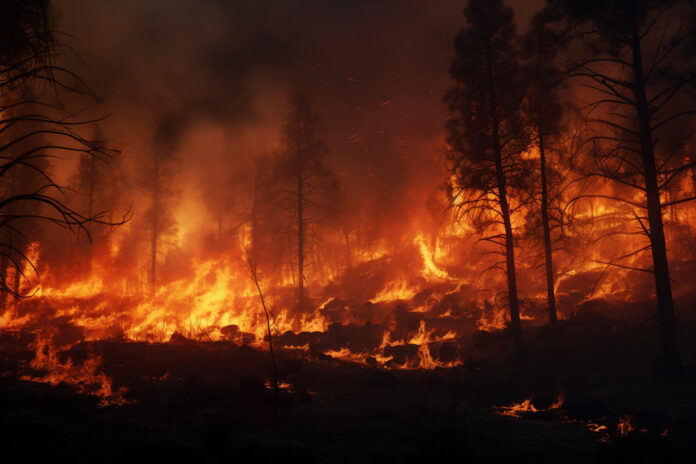
California, a state renowned for its stunning landscapes, has faced a growing crisis in recent decades: wildfires. These devastating events have not only wreaked havoc on communities and ecosystems but also raised urgent questions about climate change, land management, and preparedness. Understanding the causes, impacts, and potential solutions to California’s wildfires is essential for mitigating future disasters and protecting lives, property, and natural resources.
The Causes of California Wildfires
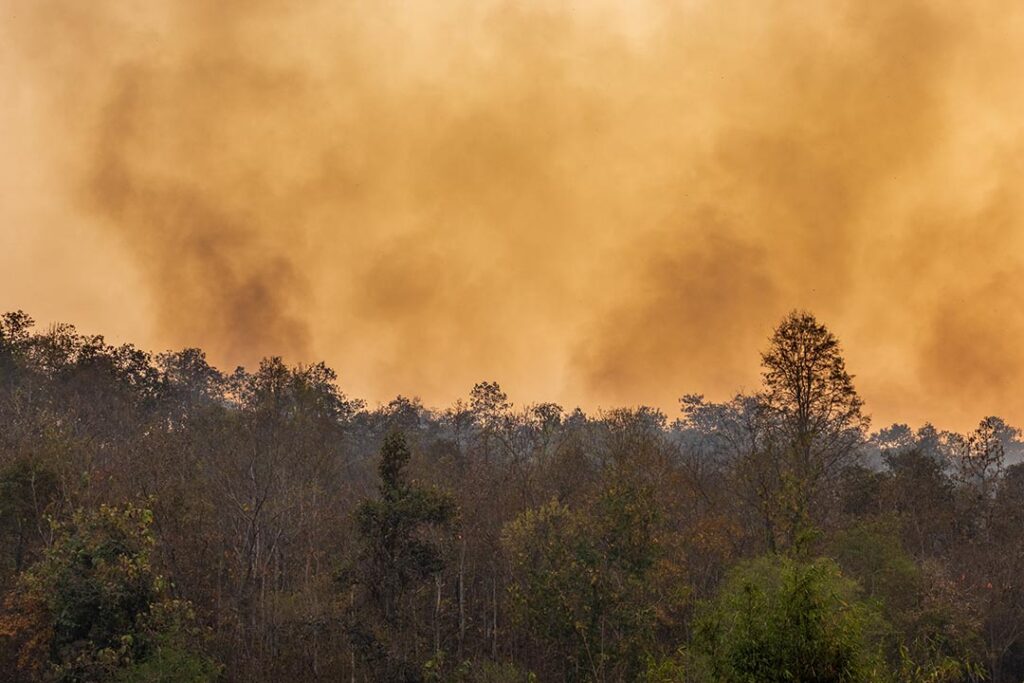

California’s wildfires result from a combination of natural and human factors, which have intensified over time. Key contributors include:
1. Climate Change
Climate change has exacerbated California’s wildfire crisis by creating hotter and drier conditions. Prolonged droughts, rising temperatures, and reduced snowpack have made forests and grasslands more flammable. Heatwaves, which are becoming more frequent, also contribute to the drying of vegetation, creating the perfect conditions for wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly.
2. Human Activity
Human activity plays a significant role in starting wildfires. Power lines, unattended campfires, discarded cigarettes, and even intentional arson have been identified as causes of many fires. Additionally, the expansion of housing developments into fire-prone areas increases the risk of ignition.
3. Santa Ana Winds
California’s infamous Santa Ana winds, which blow dry, hot air from the desert toward the coast, amplify wildfires by rapidly spreading flames. These winds can turn a small spark into a massive inferno, making firefighting efforts more challenging.
4. Poor Land Management
Decades of fire suppression policies have led to an accumulation of dry, flammable vegetation in California’s forests. Historically, smaller fires would naturally clear this vegetation, but modern suppression efforts have allowed fuel loads to build up, creating conditions for more intense and destructive fires.
The Impacts of California Wildfires
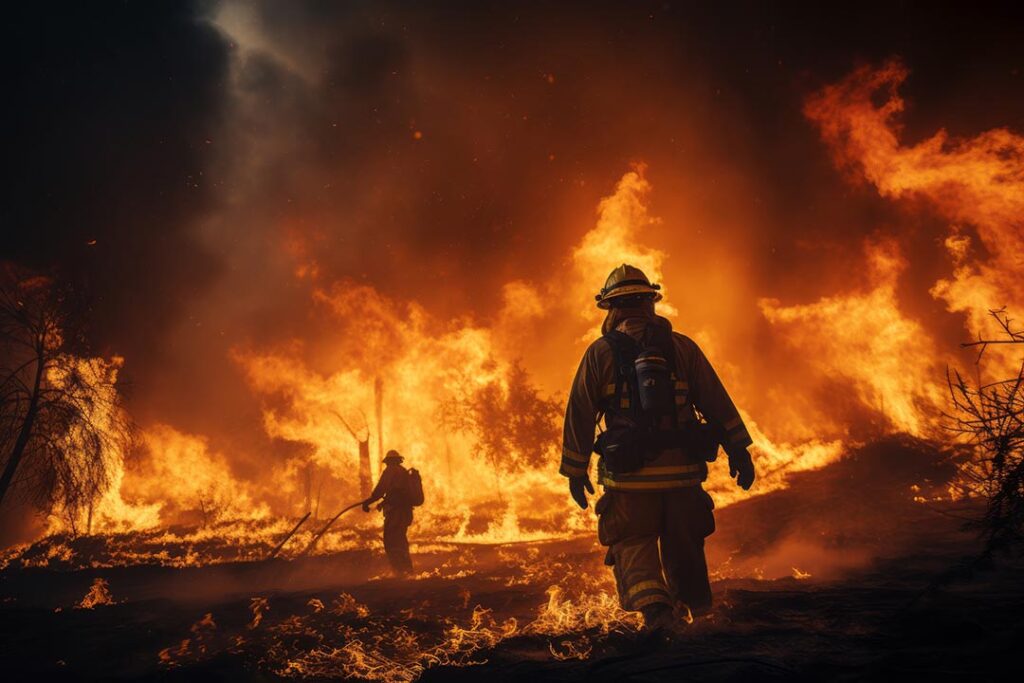

Wildfires in California have far-reaching consequences, affecting not only the environment but also public health, infrastructure, and the economy.
1. Environmental Damage
Wildfires destroy forests, grasslands, and wildlife habitats, disrupting ecosystems and causing long-term ecological damage. The loss of vegetation also increases the risk of soil erosion, landslides, and water contamination in affected areas.
2. Human Health
The smoke from wildfires contains harmful particles and chemicals that can cause respiratory problems, heart issues, and other health concerns. Vulnerable populations, such as children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing conditions, are particularly at risk. In recent years, air quality across California has reached hazardous levels during fire season, impacting millions.
3. Economic Losses
Wildfires result in billions of dollars in damages annually. Homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure are destroyed, displacing families and disrupting local economies. The costs of firefighting efforts, insurance claims, and rebuilding efforts place a significant financial strain on both the state and its residents.
4. Psychological Effects
The trauma of losing homes, loved ones, or communities to wildfires can leave lasting psychological scars. Many survivors experience anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in the aftermath of these disasters.
Notable Wildfire Events in California
California has experienced some of the largest and most destructive wildfires in U.S. history, including:
- The Camp Fire (2018): This fire destroyed the town of Paradise, claiming 85 lives and causing over $16 billion in damages.
- The Dixie Fire (2021): Spanning nearly one million acres, the Dixie Fire became the largest single (non-complex) wildfire in California’s history.
- The Thomas Fire (2017): This fire scorched over 280,000 acres and forced tens of thousands to evacuate, highlighting the challenges of combating fires fueled by strong winds.
The Role of Climate Change
Climate change is a significant driver of California’s worsening wildfire crisis. Scientists have found that the state’s average annual temperature has risen by nearly 3°F over the past century, leading to drier conditions and longer fire seasons. Additionally, warmer temperatures accelerate the drying of fuels like grasses and trees, making them more susceptible to ignition.
Research also shows that climate change has doubled the area burned by wildfires in the western United States since the 1980s. Without significant action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the changing climate, California’s wildfire risk will continue to grow.
Mitigation and Prevention Strategies

Addressing California’s wildfire crisis requires a multifaceted approach that combines prevention, mitigation, and adaptation. Key strategies include:
1. Improved Forest Management
Forest thinning and controlled burns can reduce the buildup of flammable vegetation, lowering the risk of catastrophic wildfires. These practices mimic natural fire cycles, helping to maintain healthier ecosystems.
2. Hardening Communities
Building fire-resistant homes and infrastructure in fire-prone areas can reduce the damage caused by wildfires. Materials like metal roofs and non-combustible siding, along with defensible space around properties, can make communities more resilient.
3. Early Detection and Rapid Response
Investing in advanced fire detection technology, such as satellite monitoring and AI-powered systems, can help identify wildfires in their early stages. Rapid response teams equipped with modern firefighting tools can then act quickly to contain fires before they spread.
4. Climate Action
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to renewable energy sources are critical to addressing the root causes of climate change. Policies that promote sustainable practices and increase energy efficiency can help mitigate the effects of a warming climate.
5. Public Education
Educating the public about wildfire risks and prevention measures is essential for reducing human-caused ignitions. Community outreach programs can teach residents how to create defensible space, prepare emergency plans, and respond during fire events.
The Path Forward
California’s wildfire crisis is a complex challenge that requires collaboration between government agencies, scientists, community leaders, and individuals. While progress has been made in some areas, such as improving firefighting capabilities and increasing public awareness, more work is needed to address the root causes of the problem and build long-term resilience.
Ultimately, tackling the wildfire crisis is not just about protecting lives and property — it’s about preserving California’s unique landscapes and biodiversity for future generations. By combining innovative solutions, sound policies, and collective action, California can rise to the challenge and reduce the devastating impacts of wildfires in the years to come.
In this article, we explore stories of animals reclaiming lost habitats, thriving in unusual settings, and innovative projects that foster coexistence between humans and wildlife.
Wildlife Reclaiming Habitats

One of the most fascinating aspects of wildlife behavior is how animals adapt to habitats once deemed inhospitable due to human activity. In some cases, nature reclaims what was lost; in others, animals find ways to thrive in the cracks of human civilization.
1. Wolves Return to Chernobyl
After the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear disaster, humans abandoned the region surrounding the reactor. While the area remains radioactive, it has become an unlikely haven for wildlife. Wolves, along with other animals like boars and deer, have flourished in the absence of human interference. This unexpected revival shows how wildlife can bounce back when given space, even in the most unlikely conditions.
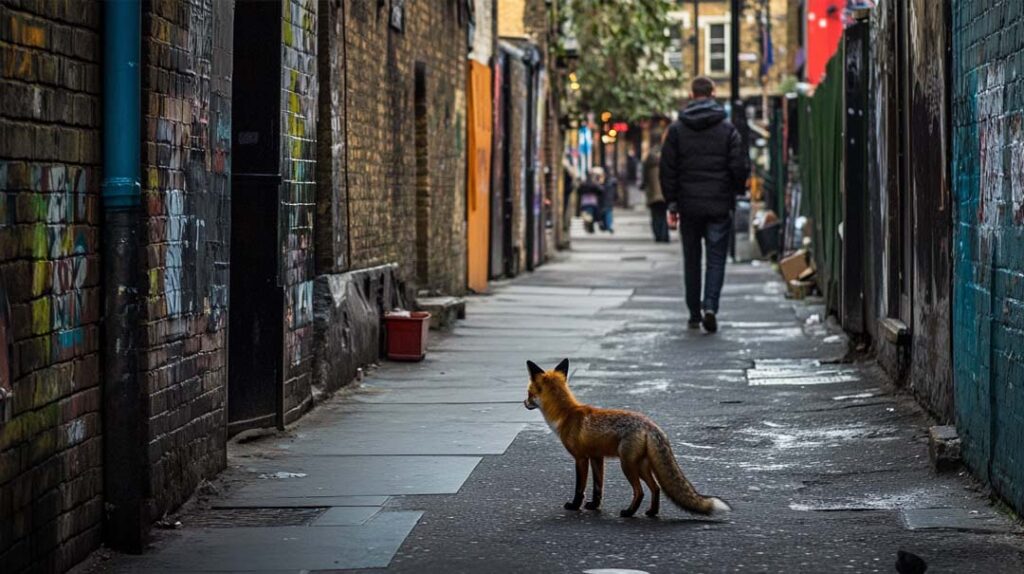
2. Urban Foxes in London
In cities like London, foxes have become a common sight, adapting seamlessly to urban life. These clever creatures have learned to navigate busy streets, scavenge from garbage bins, and even make their homes in gardens and under sheds. Their ability to coexist in such a bustling environment is a testament to their resilience and intelligence.
3. Sea Turtles in the Maldives
In some coastal areas, conservation efforts have paid off. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, reduced human activity on beaches led to a boom in sea turtle nesting. In places like the Maldives, turtles returned to previously disturbed beaches, laying eggs in record numbers. This highlights the benefits of giving nature a breather from human activity.
Thriving in Unexpected Environments
Some animals have gone beyond simply surviving and are thriving in human-altered environments. From cityscapes to industrial zones, wildlife is finding surprising ways to make the best of a challenging situation.
1. Leopards in Mumbai
The bustling city of Mumbai, India, is home to one of the highest densities of leopards in the world. These big cats live in Sanjay Gandhi National Park, which is surrounded by urban sprawl. Remarkably, they have adapted to coexist with the city’s millions of residents, hunting stray dogs and maintaining a delicate balance with their human neighbors. Conservationists are working to study this coexistence to ensure the safety of both people and leopards.
2. Peregrine Falcons in Skyscrapers
Peregrine falcons, once on the brink of extinction due to pesticide use, have made an incredible comeback. Many now nest on skyscrapers and tall buildings in cities around the world. These urban cliffs provide the perfect vantage point for hunting pigeons and other birds. The sight of falcons soaring through urban skies is a reminder of nature’s ability to adapt to even the most modern landscapes.
3. Coyotes in North America
Coyotes have become a symbol of adaptability in North America. They have learned to live in rural, suburban, and urban environments, often thriving alongside humans. In some cases, they have even altered their hunting behaviors to include scavenging and taking advantage of human-created food sources.
Coexistence Projects: Building Bridges Between Humans and Wildlife

While wildlife has shown remarkable adaptability, it is crucial for humans to support coexistence rather than exacerbate conflicts. Around the world, projects are being implemented to foster harmony between people and animals.
1. Elephant Corridors in India
In India, conflicts between elephants and humans are a significant issue, as development often encroaches on traditional elephant migration routes. To address this, conservationists have created “elephant corridors” — protected pathways that allow elephants to move safely between habitats without disrupting human settlements. These corridors have reduced human-elephant conflicts and ensured the survival of these majestic creatures.
2. Beehive Fences in Africa
Farmers in Africa often face challenges from elephants raiding their crops. A simple yet effective solution has emerged: beehive fences. Elephants are naturally afraid of bees, so placing beehives along the borders of fields acts as a natural deterrent. This approach protects crops while also providing farmers with an additional source of income from honey production.
3. Urban Wildlife Corridors in the United States
In cities across the U.S., urban planners are designing wildlife corridors to help animals move safely through urban areas. For example, in Los Angeles, the Liberty Canyon Wildlife Crossing is a bridge over a busy freeway that allows mountain lions, coyotes, and other animals to traverse safely. These projects not only prevent accidents but also preserve genetic diversity by connecting isolated populations.
4. The Return of Beavers in Europe
Beavers are being reintroduced in parts of Europe as natural ecosystem engineers. Their dams create wetlands, which support diverse species and improve water quality. In Scotland, reintroduced beavers have transformed degraded habitats into thriving ecosystems while also helping to mitigate flooding.
The Lessons of Wildlife Resilience
The stories of animals adapting to human encroachment are both inspiring and sobering. They remind us of the resilience of nature but also highlight the pressures humans place on the natural world.
By creating opportunities for coexistence, such as protected corridors, conservation projects, and sustainable development practices, humans can help ensure that wildlife continues to thrive. At the same time, we can learn valuable lessons from nature’s adaptability — lessons about resilience, balance, and the interconnectedness of all living things.
As wildlife reclaims its space and adapts in extraordinary ways, it is a reminder that the natural world is not separate from us. It is part of our shared home, and its survival is intertwined with our own. In embracing coexistence, we not only protect wildlife but also preserve the beauty, diversity, and vitality of our planet for future generations.